Articles
Foot Pressure Scan | Best Type of Foot Scan
The best type of foot scan involves using a pressure platform with tactile sensors to capture all characteristics of the foot and analyze its function. Foot Pressure scan is done to measure and analyze a person’s feet while they are performing activities such as walking, running, and standing. It performs by using an advanced device to produce a clear picture of the pressure applied to each part of the foot sole. This type of scan is very useful for foot specialists, as it can determine the exact location of any extra pressure on the foot.
The contents and facilities in this article are described according to the facilities available in Payatek’s PT-SCAN foot pressure scanner.
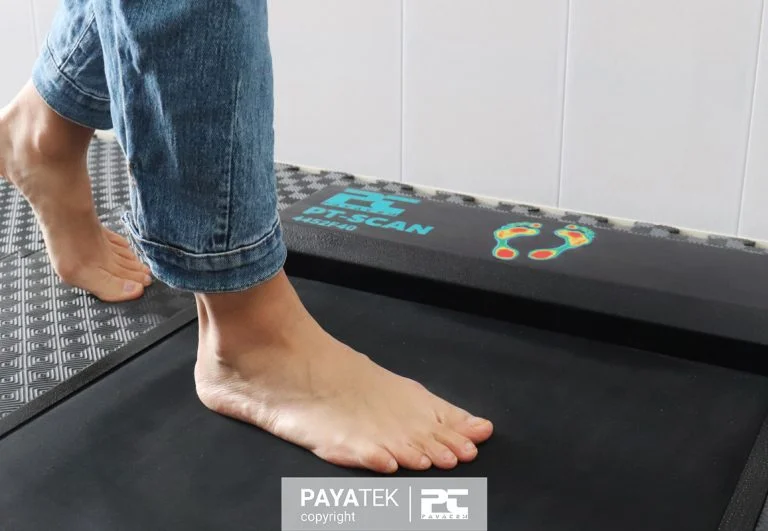
How is the plantar scan performed with the foot pressure scanner?
Scanning the sole of the foot with a foot pressure scanner is a very simple, comprehensive, and reliable method that requires only a few minutes to perform. Foot Health Practitioners (FHP) scan the feet’ soles in three ways: static (for a standing person), dynamic (for a walking person), and static balance. When someone runs or walks on the pressure-sensing mat, the pressure that is distributed on different areas of the sole is captured.


The pressure scanner is connected to the computer, and information about the foot pressure distribution is displayed. The sensors in the pressure scanner evaluate the forces applied from the foot sole to the pressure sensing mat, which is then displayed in the form of a graph. The various diagrams of this device provide a detailed description and interpretation of foot health and the characteristics of a person’s steps.
Why should a foot scan be done with a foot pressure scanner?
You may be surprised by the process of scanning with a foot pressure scanner. This process has several advantages, and being aware of them will help you.
Simple performing for the patient
This test is performed on patients by having them walk and stand on a flat surface, such as a carpet or rug. There is also no need to place the foot in a special position on the device.
Accurate and comprehensive analysis
The analysis is very accurate and comprehensive, as it shows a detailed distribution of weight bearing on the foot; foot sole pressure measurement is done point-by-point; and it provides a comparison of the pressure distribution between the two feet.
Evaluate the position of the body’s center of force
The body’s center of force is evaluated by scanning it with a foot pressure scanner while standing and walking. This is an accurate tool that assesses the health of the lower limbs and identifies any musculoskeletal system issues.
Kinesiology diagrams and monitoring the treatment process
Foot pressure scanning with a pressure mat provides a comprehensive study of a human’s kinesiology. The balance screen charts enable specialists to measure the health condition of the scanned foot compared to an ideal, perfectly healthy foot (without taking into account the weight and size of the foot). Consequently, the treatment effectiveness and aids (orthotic insoles and braces) can be easily compared and checked. As a result, the treatment process and recovery are always under the control of a specialist.
Examining chronic and localized pains
Chronic pains in the foot sole can be assessed using a foot pressure scanner. People who feel pain when they start walking or feel pain after walking have chronic or localized pain. As a result, they need a gait analysis to check for the cause of this pain. For these people, orthotic insoles are made according to the results of the foot scan during walking.
Is the foot pressure scanner providing us with accurate data?
Human foot pressure must be applied to a platform in order to capture the foot pressure. Pressure sensors are therefore required in the device used for performing foot scanning. It is not accurate to measure the foot pressure using scanning technology and just in a standing position that simply captures the foot sole pressure; only approximate findings can be obtained. For more accurate results, foot scanning should be performed while walking (gait cycle), too.


Foot pressure scanning and back pain
The cause of many back pains is an unbalanced distribution of pressure in the feet, or foot pressure asymmetry. Therefore, in order to diagnose and treat the various conditions caused by this unbalanced distribution, it is necessary to analyze the foot pressure with a foot pressure scanner.
Foot pressure scanning for peripheral neuropathy
Foot pressure has a direct impact on how you walk. An easier way to describe this is the posture you take when you walk, stand, or run. This effect is caused by supporting the feet and reducing pain or increasing comfort when standing or walking. A foot scan with a foot pressure scanner is important for the evaluation of patients with peripheral neuropathy. Peripheral neuropathy, a result of damage to the nerves located outside of the brain and spinal cord (peripheral nerves), often causes weakness, numbness, and pain, usually in the hands and feet. Sometimes it can result in foot pressure asymmetry. Therefore, scanning with a foot pressure scanner provides the orthotic specialist with the necessary information to treat the patient.
Foot scan for lower limb and foot pain
Certain conditions, such as diseases of the musculoskeletal system, often cause peripheral muscle weakness. This concept involves an uneven distribution of strength throughout the body, leading to difficulty walking and eventually pain in the lower limbs. A foot pressure scanner can provide the specialist with the necessary information about pressure distribution, allowing them to prescribe treatment and relieve pain based on such conditions.
Scanning the athlete’s feet
Performing a scan with a foot pressure scanner is extremely important for the diagnosis and treatment of various lower-limb complications. This is also necessary for athletes, as their knowledge and awareness of the pressure distribution of the foot sole increases their understanding of their bodies and significantly improves their performance. As a result, it ensures that they do not injure themselves.