Posture is important for balance. It is the position in which we hold our bodies while standing, sitting, or lying down. Correct bodily alignment maintained by the appropriate level of muscular tension in opposition to gravity is the foundation of good posture. Our regular motions and activities can alter this alignment and put stress on our muscles and joints, which can occasionally cause pain and eventually lead to permanent injury if left untreated. The use of the right mobility and ergonomic techniques can aid in the prevention of these issues.
Poor posture can cause a wide variety of issues, starting with giving you a slouchy look. Furthermore, it puts too much strain on your muscles and joints, which can lead to fatigue and chronic discomfort depending on which part of your body is affected the most by your posture.
What are the complications and symptoms of poor posture?
Many of us suffer from poor posture due to the little knowledge we have about the proper posture and this weakness manifests itself in various ways, including symptoms that many of us may not know:
Many of us have poor posture because we don’t have enough information on good posture. It shows up in a variety of ways, including with symptoms that many of us might not be aware of:
- Lack of muscle tolerance or lowering of muscle fatigue threshold
- Headache
- Painful menstruation
- Increased pressure on muscles and joints
- Arthritis and…
If you would like to get acquainted with the types of postural abnormalities, refer to the article “Introduction of Postural Abnormalities”.
Symptoms of poor posture
These parts of the body are most affected by poor posture
- neck
- shoulders
- spine
- hips
- back muscles
- abdominal wall
and you may feel some or all of these symptoms on that area
- Pain
- Stiffness
- Reduced range of movement
- Muscle spasms
- Numbness
- Tingling/pins and needles
- Gait problems
- Balance problems
Disease can cause by bad posture
Spinal misalignment and disease are more closely connected than most people realize. Slumping or slouching not only makes you seem unpleasant, but it can also seriously affect your health. The spine’s ability to maintain balance and absorb shock is affected by poor posture. Here are some of the injuries and diseases that poor posture is correlated with:
- Headaches
- Back pain
- spinal dysfunction
- joint degeneration
- rounded shoulders
- Arthritis
- Painful menstruation
- high blood pressure and other heart disease symptoms causes by stress
- breathing difficulties
- worsen seasonal allergies
- sexual dysfunction
How is proper posture in sitting and lying position?
Proper sitting posture
For most of us, sitting is a crucial part of our days, so maintaining an appropriate sitting posture can greatly reduce any potential risks. Correct posture when sitting ensures that you are putting less strain on your back muscles.
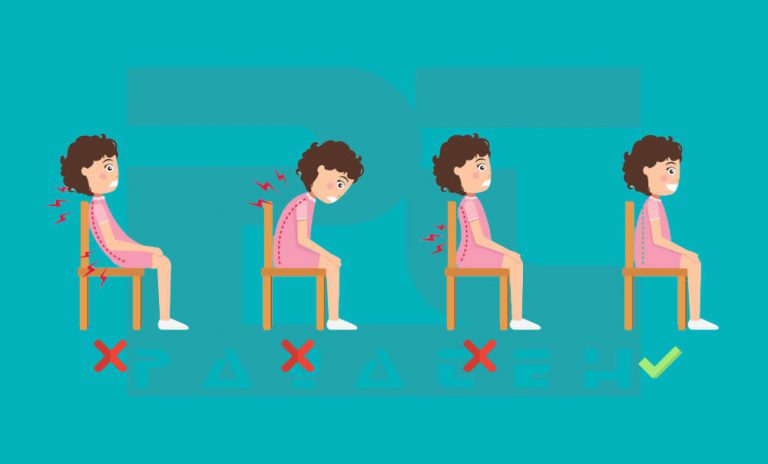
Even a few hours of bad posture sitting each week can cause back, neck, and shoulder pain. In fact, poor posture can alter the structure of your spine and lead to health problems such as back and neck pain, headaches, poor balance, etc. So, finding the right posture is crucial, especially while spending all day at a desk. You can start working on correcting your posture by choosing ergonomic products like a chair, mouse, mouse pad, monitor stand, or even a stand-up desk.
Some common errors to avoid while sitting:
- Placing your buttocks close to the edge of the seat by slouching into the chair
- Spending a lot of time swaying to one side
- Sitting without lumbar support to prevent back pain
- Cross your legs, knees, or ankles
- Instead of rotating your whole body or chair, rotate your spine to complete a task
- Slump over and rest your elbows on your desk
- Slump to one side
- Sitting for more than an hour (Take a 10-minute break every hour and get up and move.)
- Sitting on a chair that has poor support for your body or stability
- Dangling feet
- Excessively arching the lower back
- Keeping elbows far from the body
- Cramming thighs under a worktable will affect blood circulation
Proper Sleeping Posture
According to research, posture in the sleeping position, the quality of sleep, and general health are all related. Your entire health will improve and your sleep will be optimized if you can find the right sleeping posture for you.
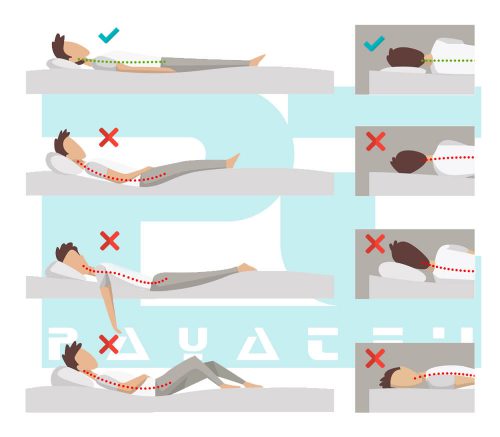
Choosing to sleep on your back, side, or stomach may place pressure on certain body areas, including the spine, or have an impact on some bodily processes, such as digestion. Therefore, depending on your state, the way you sleep might either benefit or harm your health.
Sleeping on the back
In general, it’s best to sleep on your back at night to maintain proper posture. But thicker pillows can really make your neck hurt. In order to prevent your neck from overextending, try using a little pillow, or maybe none at all. A little pillow placed beneath your knees can also be a good option if you suffer from low back problems. The best position to be in while lying down is with your arms spread out to the sides, low back flat, and shoulders tucked back.
Sleeping on the side
Adults generally prefer to sleep on their sides, which has many advantages. People who snore or have other sleep-related breathing problems, such as obstructive sleep apnea, are sometimes advised to sleep on their side. As this position helps relieve strain on the spine, sleeping on one’s side may also help reduce neck and lower back problems.
Whether a person has certain health issues may also influence whether they choose to sleep on their left or right side. People suffering from heart failure, for example, may discover that sleeping on their right side improves their breathing. On the other hand, compared to lying on their left side, patients with acid reflux typically experience worse symptoms when doing so.
Sleeping on the stomach
Sleeping on the stomach is less common among adults. Stomach sleeping can put a strain on the spinal column and increase the risk of back and neck problems. Additionally, the limited chest mobility in this posture might make breathing more difficult and require more energy from the body. Regarding the heart, sleeping on the stomach causes a higher heart rate and more effort to lift the body against gravity.
When you lie in bed, you should make an effort to maintain alignment in your hips, shoulders, and ears. You can help your alignment by placing a cushion beneath your stomach or pelvis. Avoid bending at the waist while moving at night. Move your entire body at once to maintain good spinal alignment.
Causes of poor posture

Poor posture can occur for a variety of reasons, some of which are as follows:
- muscle tension or weakness
- poor footwear
- genetic conditions
- injury
- over-use of technology like mobile phones, televisions, computers, and tablets
- fatigue
- carrying heavy bags or purses
- carrying extra body weight
- sleeping position
- stress and anxiety
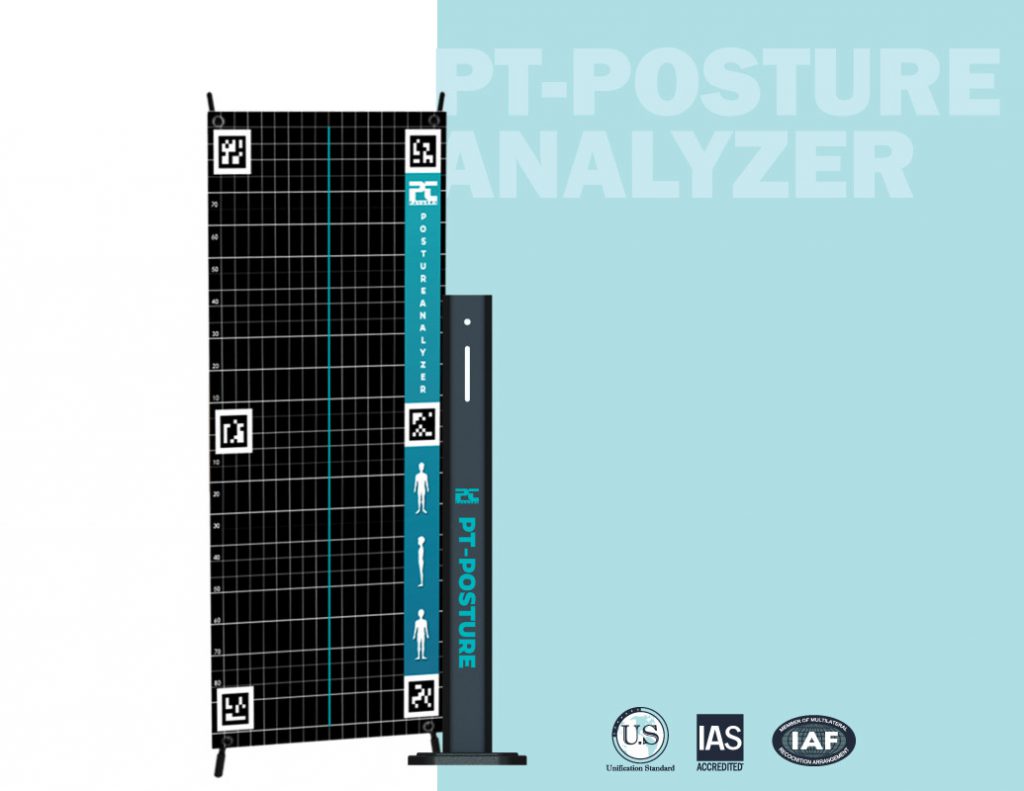
Diagnosis of poor posture
An expert can diagnose a bad posture or a posture abnormality in two ways. One of the methods is visual evaluation. The next method is to use the posture analysis device, which uses photogrammetric technology, to evaluate the characteristics of stature, the anomalies of the spine and skeleton of the human body, the asymmetries in the human body, and the deviations of the axis of the human body.
How to correct?
Visit a specialist in physical medicine and rehabilitation, technical orthopedics, physiotherapy, and biomechanics to analyze the posture condition. They analyze your posture and can detect any abnormalities. Then the treatment process will begin after the assessment.
Some suggestions to correct poor posture:
- stretch and strengthen the muscles in your upper back, chest, and core with related exercises
- exercise and tone your abs
- holding your head upright, in line with your spine
- keeping your shoulders back and chest forward
- maintain a healthy weight
- keep the body in alignment while sitting in an office chair and while standing
 فارسی
فارسی