Supination and pronation is one of the common problems in the foot anatomy that causes pain. They are parts of the gait phase (including two steps). Supination occurs when the weight tends to be more on the outside of the foot while walking or running. On the other hand, when the weight tends to be more on the inside of the foot while walking or running, pronation occurs. These problems are accurately evaluated and identified by foot pressure scanners and gait analysis devices. The more important thing than the identification of the problems is the effect of them on the person’s gait and the skeletal system, which is determined in the dynamic analysis of these devices.
Excess supination (underpronation) and excess pronation (overpronation) can cause problems in weight balance and cause foot, knee, and back pain.
In the next sections, you will learn about the treatment and prevention techniques for people who have excess supination.
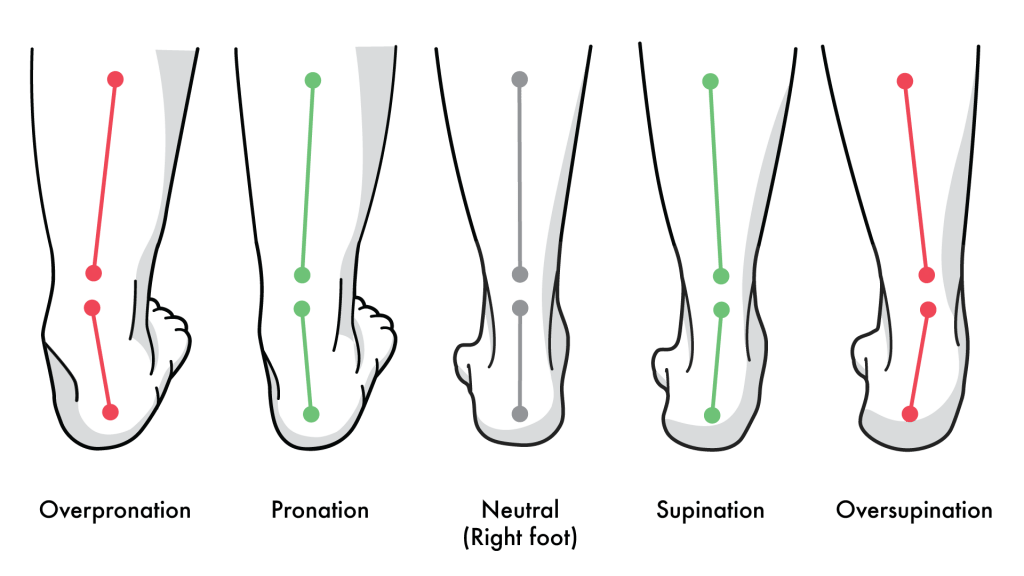
In the picture above, you can see supination and pronation, where the weight bearing is on the outer and inner of the ankle and your feet lean in (pronation) or out (supination).
Some points about supination and pronation:
- Too much supination can cause problems such as pain and abnormal posture
- Most people with excess supination have structural foot problems
- The methods of diagnosis and examination of this problems include eye examination, plantar pressure scan and gait analysis
- Using right shoes and personalized insoles for prevention and treatment
1. Excess supination and pronation
The person’s foot with excess pronation rolls toward the inside and the arch tends to flatten out, which causes the inner part of the heel to be in contact with the ground and causes flat footed.
People who do not roll their feet inward enough have supination. This puts pressure on the ankle and rotates it outwards, which increases the risk of sprain and causes injury.
Excess pronation is much more common than excess supination.
2. Causes of supination
Foot problems that cause supination are usually congenital. But external factors can also play a role in creating these conditions.
Common causes of excessive supination include:
2-1. Genetics
Features affecting foot mechanics, which are often congenital, include:
- Leg length (including leg length difference)
- foot width
- Ankle stability
The shape of the foot arch may also affect the risk of causing supination, as runners with a high arch are more to developing supination prone than other runners.
2-2. Improper shoes
Choosing the right shoes is so important in maintaining the health of the foot and the skeletal system. Orthotics or special shoes shoe supports the arch and soft part of the foot, and this protects the foot from possible injuries. The effect of proper orthotic shoes is more evident when walking on hard and smooth surfaces. We suggest you read the article “Foot Health and Orthotics Shoes” to learn more about the diseases associated with the use of improper shoes and the important features in choosing the right shoes. Choosing the improper shoes—such as rigid or tight shoes—can cause supination and other foot problems. Wearing shoes that are very old and do not support the arch can also cause supination.

2-3. Bodily misalignment
If the human body structure is not in the right and balanced position, other body parts must be under more pressure to compensate for this problem, to support the correct body structure and maintain the balance of the body. Read the article ” The introduction of postural abnormality types, what are the symptoms, ways to prevent and treat these abnormalities?” to learn more about postural abnormalities.
Bad or poor posture during sports training can cause problems in muscles and bones, resulting in supination. For further reading, please refer to the article “Assessment of Athletes’ Posture Status”.
The problems of the skeletal system can be evaluated using the posture analysis device.
2-4. Old injuries
Old injuries can cause instability and weakness in bones and soft tissue in the body. For example, especially people with Achilles Tendonitis are at risk of supination.
2-5. Other reasons
Some other factors that can cause supination:
- sedentary lifestyle
- constant impact on hard and firm surfaces
- restricted range of motion
- standing for long periods of time
- stiffness due to aging or arthritis
- too much exercise
3. Complications of excess supination
People with excessive supination are prone to the following problems and symptoms:
- Ankle pain and sole pain
- Ankle sprain
- Callus or bunions on the outer edge of the foot
- Hammertoes or clawed toes
- Iliotibial band pain syndrome
- Pain in the ball of the foot
- Plantar fasciitis
- Shin splints
- Fracture and cracking caused by excessive pressure or so-called stress fracture
- Swelling of the ankle or foot
- Weakness of the foot and ankle muscles that gets worse when running, walking or standing

4. Diagnose and examine supination
The following techniques can help indicate excessive supination of the foot:
4-1. Check your old shoes (shoe abrasion)
The sole of the shoe wears down from the outer edge of the heel towards the center in people with normal gaits who do not suffer from excessive supination or excessive pronation.
Supination causes abrasion only on the outer edge of the shoe sole. Therefore, the presence of abrasion on the outer edge of the shoe and the absence of abrasion in the center of the shoe can be a sign of excessive supination.
4-2. Checking footprints on the ground
Wetting the soles of bare feet and walking on a flat surface can help diagnose gait problems. To do this test, you must perform the following steps:
- Get wet your feet
- Step slowly on the surface that shows the footprint. The best surfaces are a cement surface or a brown paper bag
- Taking the foot off the surface and checking the footprint
If half of the arch is visible on the surface, it is considered a normal foot pattern. If only a small part or none of the arch is outlined, it is considered supination.
It should be noted that this method is completely qualitative and depends entirely on the specialist who is performing the test and does not have enough accuracy.
4-3. Foot scan with gait analysis device
A podiatrist or a physical therapist can diagnose this abnormality in the foot by performing a gait analysis test. It involves the person walking or running on a plantar pressure scanning platform.
People who experience one of the signs or issues of excessive supination of the foot or who notice supination following the old shoe test or the wet foot test must perform a gait analysis test under the supervision of a podiatrist or a sports therapist who is trained to diagnose and treat foot issues.
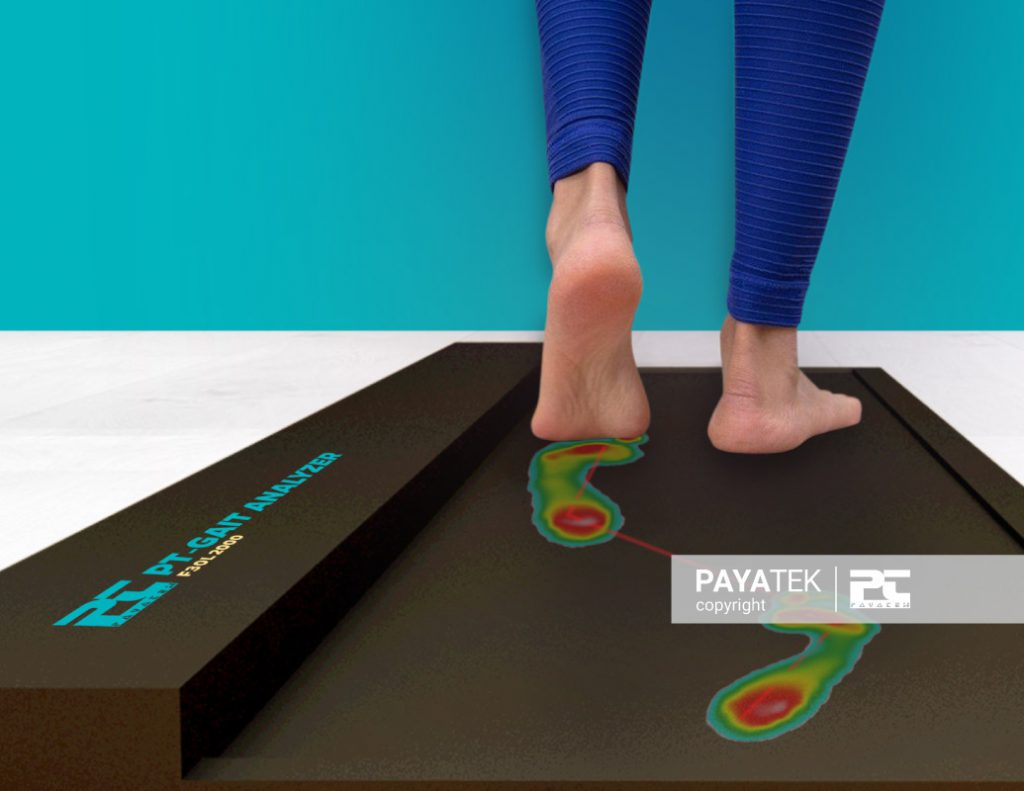

5. Prevention of foot supination
Foot supination can be prevented or corrected by the following ways:
5-1. Appropriate shoes or orthopedic shoes
Walking and running shoes that are lightweight, flexible, with extra cushioning and ample room in the toes are the best options for people with supination. Consulting with a pediatrician and specialist to suggest a suitable shoe for supination treatment can also be very helpful.
Guide to buy shoes:
- Measure both feet for length, width, and depth to find the best fit
- Wear socks that you use while walking or running
- Look for shoes with good shock absorption, arch support, and enough room in the toes
- Go shopping in the evening and at night, when the foot is at its largest size
- Do not select tight shoes in the hope that they will loosen over time
You should replace your running shoes. As a general rule, you should change your running shoes every 300–500 miles or every 500 to 750 kilometers.
5-2. Appropriate orthoses
Right shoes designed for supination can support the arch and heel to control foot movement. Special orthoses for supination can be prepared and manufactured through stores or specially designed by specialists.
We have explained more about this in the article “Four reasons to use orthotics Insole!”
5-3. Correct running and walking form
Correcting spinal deformities and incorrect techniques during running and walking is very important to correct excessive supination. Spine pain can be a serious alarm.
If you are interested in running, we recommend read the article “How to run better?” What are the ways to increase the recovery and performance of the feet while running?”
When running or walking, try to land lightly on your feet and try to keep the midfoot more in touch with the ground than the heel. The best way to land with flat feet is to avoid curling your toes. Taking shorter steps makes it easier to maintain proper form while running and walking.
5-4. Podiatrist
A podiatrist can help the foot muscles and tendons become flexible as well as strengthen the soft tissues of the foot. This helps better weight distribution throughout the body, which corrects supination.
5-5. Corrective exercises and movements for supination
The following exercises can help with the flexibility and strength of the muscles that create normal gait:
5-5-1. Calf muscle stretch
1- Place your hands on the wall.
2- Step one leg back a few feet, keeping both feet on the floor.
3- Keeping the back leg straight, bend your front knee until you feel a stretch. In this position, you should feel a stretch along your back leg’s calf muscle and along the back of your ankle.
Continue the stretch for 30 seconds. And repeat this movement three times.
5-5-2. Plantar fascia stretch
1. Sit in a chair
2. Cross your left ankle on the right knee
3. Grab your toes with the left hand and slowly pull them towards the front of your ankle. You should feel a stretch in this area.
5. Hold this stretch for 10 seconds.
Repeat 20 times for each foot.
The American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons recommends that people repeat this exercise every morning for best results.
5-5-3. Knee stretch
1. In a standing position, cross the right leg behind the left.
2. Keeping your hips level, bend to the left. Do not bend forward or backward. You should feel a stretch on the outside of your right knee and thigh.
4. Hold the stretch for 10 seconds and repeat this movement three times for each leg.
6. Conclusion
Although supination and pronation are natural parts of movement, a large amount of each of these two movements causes an asymmetric gait and as a result, problems such as foot pain, back pain, foot swelling, swelling of the muscular system, lack of proper body alignment and there are many problems in the musculoskeletal system of the body.
Using orthotic shoes, orthotic insoles, and a commitment to regular stretching can be helpful.
If a person experiences pain or swelling in the foot or ankle for more than a few days, he must refer to pediatricians to perform a gait analysis test to check supination. The specialist may also perform additional tests to check for other common problems in the ankle and other parts of the foot.

PayaTek
Foot Pressure Scanner
 فارسی
فارسی